DATE2024.01.11 #Press Releases
Toward efficient spintronic materials
Researchers reveal how magnetization direction can be controlled using strain in an interfacial multiferroic material.
Jan 11, 2024
Controlling the direction of magnetization using low electric field is necessary for developing efficient spintronic devices. In spintronics, properties of an electron’s spin or magnetic moment are used to store information. The electron spins can be manipulated by straining orbital magnetic moments to create a high-performance magnetoelectric effect.
Japanese researchers, including Jun Okabayashi from the University of Tokyo, revealed a strain-induced orbital control mechanism in interfacial multiferroics. In multiferroic material, the magnetic field can be controlled using an electric field—potentially leading to efficient spintronic devices. The interfacial multiferroics that Okabayashi and his colleagues studied consist of a junction between a ferromagnetic material and a piezoelectric material. The direction of magnetization in the material could be controlled by applying voltage.
The team showed the microscopic origin of the large magnetoelectric effect in the material. The strain generated from the piezoelectric material could change the orbital magnetic moment of the ferromagnetic material. The team revealed element-specific orbital control in the interfacial multiferroic material using reversible strain and provided guidelines for designing materials with a large magnetoelectric effect. The findings will be useful in developing new information writing technology that consumes less power.
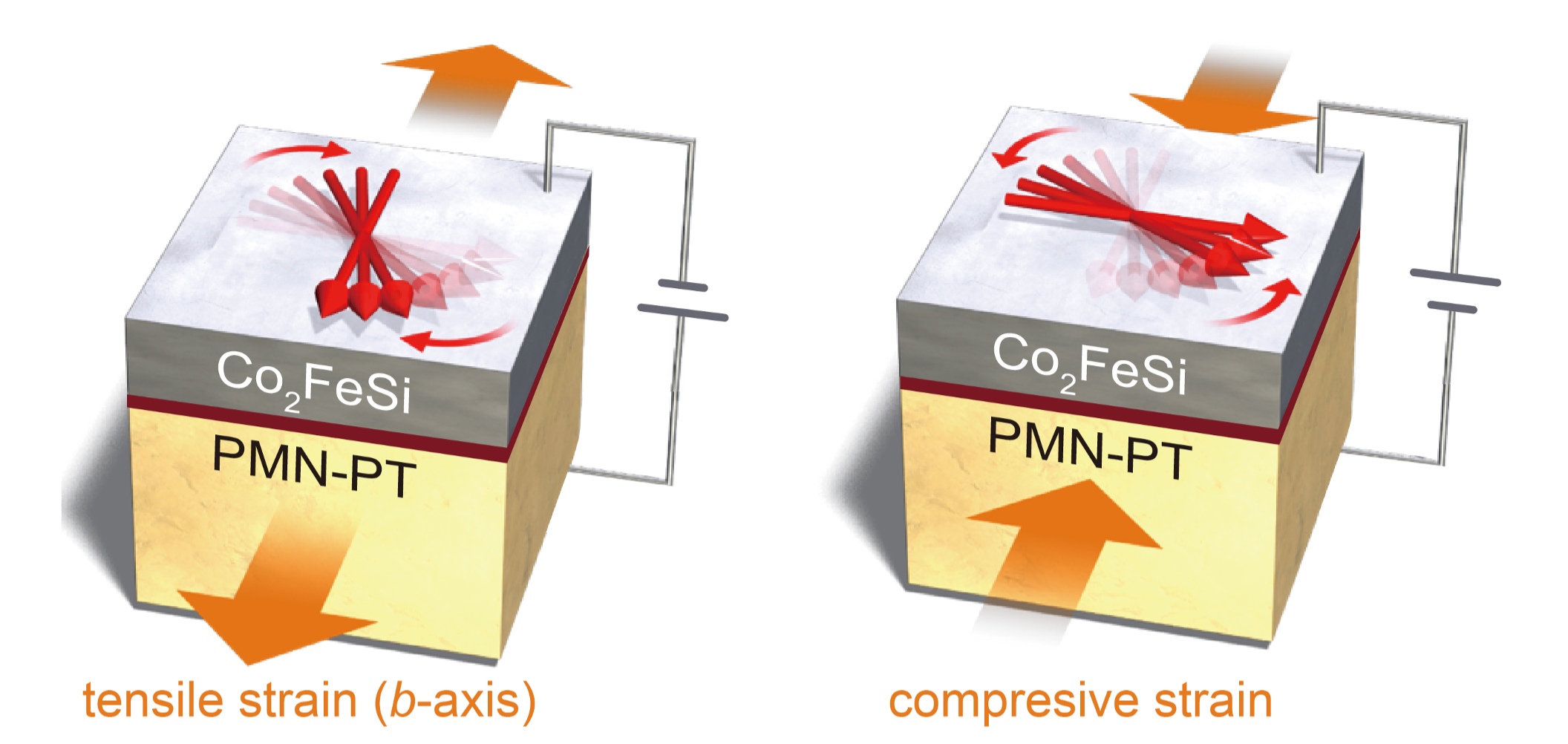
Figure: Interfacial multiferroic structure and control of magnetization orientation.
For more details, please read the article:
Jun Okabayashi, Takamasa Usami, Amran Mahfudh Yatmeidhy, Yuichi Murakami, Yu Shiratsuchi, Ryoichi Nakatani, Yoshihiro Gohda, and Kohei Hamaya. 2024. Strain-induced specific orbital control in a Heusler-alloy-based interfacial multiferroics. NPG Asia Materials. DOI: 10.1038/s41427-023-00524-6


