DATE2023.12.07 #Press Releases
Cryo-EM Analysis Elucidates the Mechanism of Glucose Uptake into Cells by SGLT2
Disclaimer: machine translated by DeepL which may contain errors.
Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation
Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo
Summary of Presentations
Professor Nureki Osamu, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, in collaboration with Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, a member of the Mitsubishi Chemical Group, has succeeded in high-resolution cryo-EM analysis of SGLT2 -inhibitor complexes and elucidated the mechanism of sugar uptake into cells. The research results were published in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology on December 6, 2023.
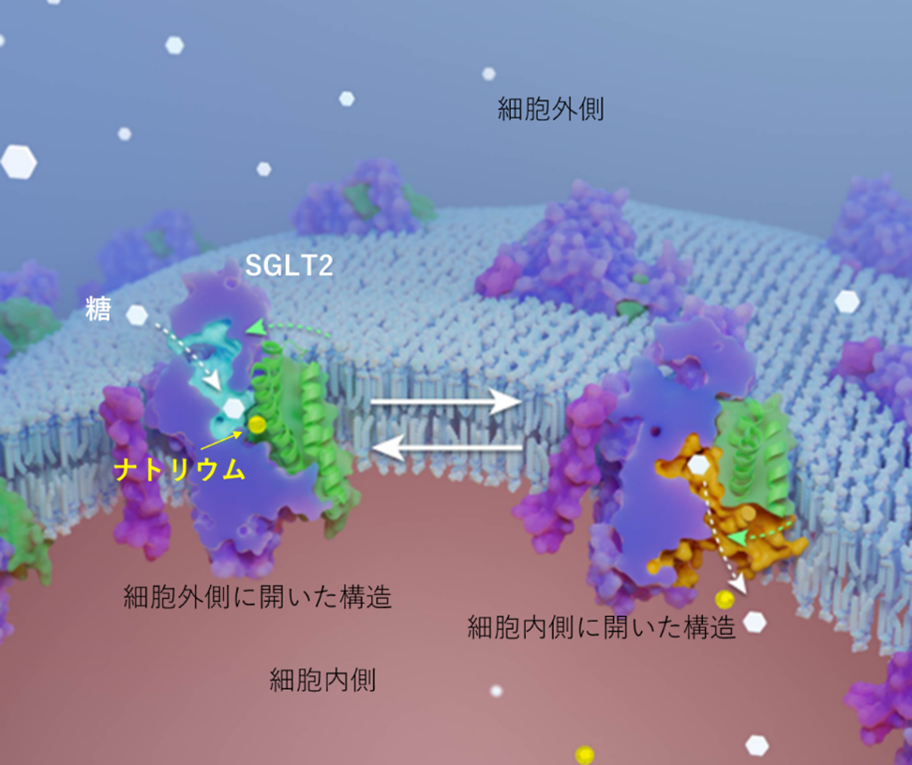
SGLT2 inhibitors are drugs for type 2 diabetes that lower blood glucose levels by inhibiting SGLT2, a transporter that reabsorbs sugar in the renal tubules. In this joint research, the complex structures of SGLT2 protein and various types of SGLT2 inhibitors (four glyflosine compounds and a natural product, phloridzine) were analyzed using cryo-EM. The results revealed that the glyflosine compounds (SGLT2 inhibitors) bind to sugar-binding sites on the extracellular side of the cytoplasmic structure where sodium binds, whereas the natural product phloridine, which was the starting point for drug discovery, binds to sites on the cytoplasmic side of the intracellularly open structure where sodium does not bind The natural product phloridine, which was the starting point of drug discovery, binds to sites on the cytoplasmic side of the open intracellular structure where sodium does not.
Based on the findings from this structure, and adding experimental data from transporter function analysis technology to the discussion, it was clarified that when SGLT2 transports sugar, sodium is the starting point of the conformational change, and sugar uptake occurs when sodium is dislodged. (Figure below)
For more information, please visit the website of Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation.
Journal
-
Journal name Nature Structural & Molecular BiologyTitle of paper


