DATE2023.10.20 #Press Releases
How do plants adapt to changing environments?
A study reveals the molecular mechanisms underlying the regulation of developmental plasticity in plants.
Oct 20, 2023
Plants change how they grow depending on the changing environment. That’s why you see autumn colors or spring flowers as plants respond to temperature and weather conditions. Researchers from the University of Tokyo probed the molecular mechanisms of this developmental plasticity in a well-known model plant called Arabidopsis thaliana.
Plants respond to the environment thanks to the expression of genes and the regulation of the gene expression. Modification of histone proteins that bind DNA to form chromatin structures is a way to regulate gene expression.
The research team discovered that an enzyme called LDL3 (a histone demethylase protein) plays a major role in histone modification. They used machine learning to find the genes that LDL3 targets. LDL3 protein cooperates with the transcription complex (a protein complex involved in DNA transcription to RNA) to remove H3K4me2, a modification of histone proteins regulating the expression of many plant genes. This negative interaction between the LDL3 protein and the H3K4me2 is unique to plants.
The team concluded that LDL3 protein plays a major role in plant developmental plasticity. The findings could help them create plants that are resistant to environmental changes, which would be beneficial in solving problems related to agriculture and climate change. 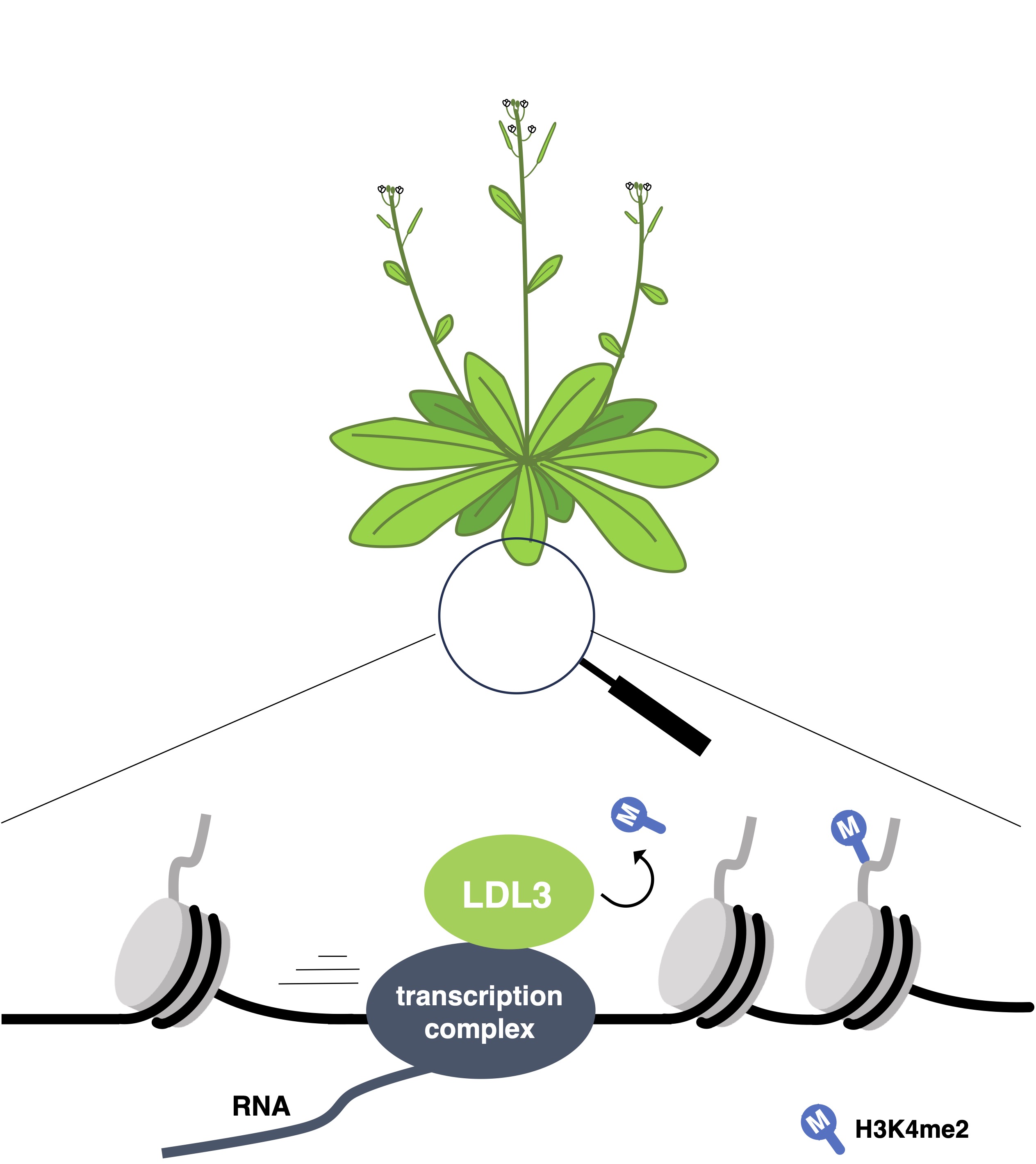
Figure: A schematic of the molecular mechanism involved in plant developmental plasticity.
For more details, please read the article:
Shusei Mori, Satoyo Oya, Mayumi Takahashi, Kazuya Takashima, Soichi Inagaki,Tetsuji Kakutani. Cotranscriptional demethylation induces global loss of H3K4me2 from active genes in Arabidopsis. EMBO Journal. DOI: 10.15252/embj.2023113798


